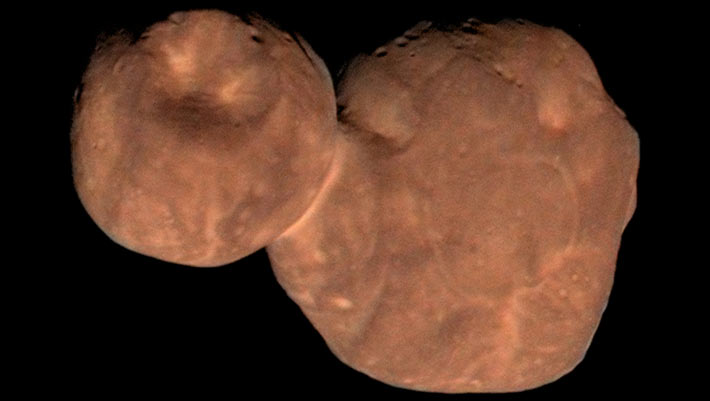
Study: Jupiter’s Moon Io Has Been Volcanically Active for All of Its History
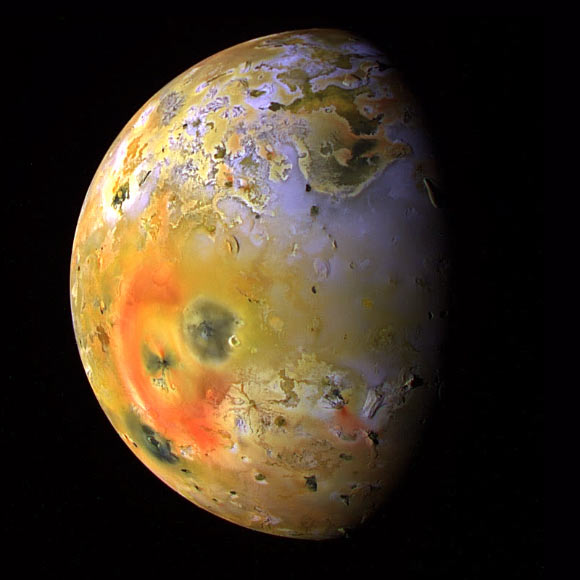
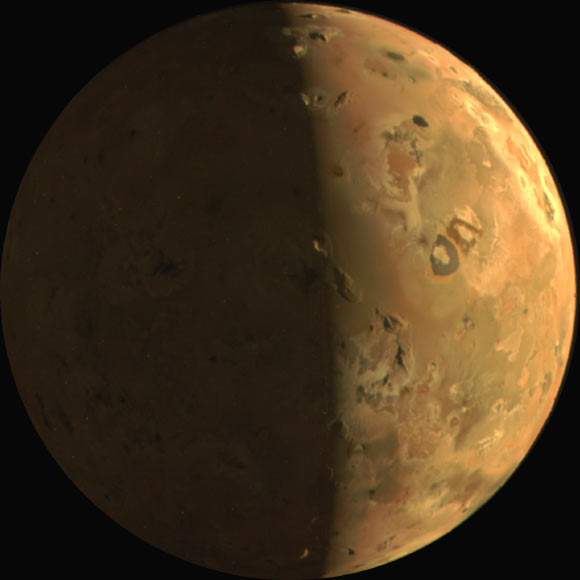
Sulfur and chlorine isotopes in Io’s atmosphere indicate that it has been volcanically active for the entire 4.57 billion-year history of the Solar System. This global view of Io was…