Study: Asteroid Psyche Originated beyond Solar System’s Snow Line and Later Migrated to Main Belt
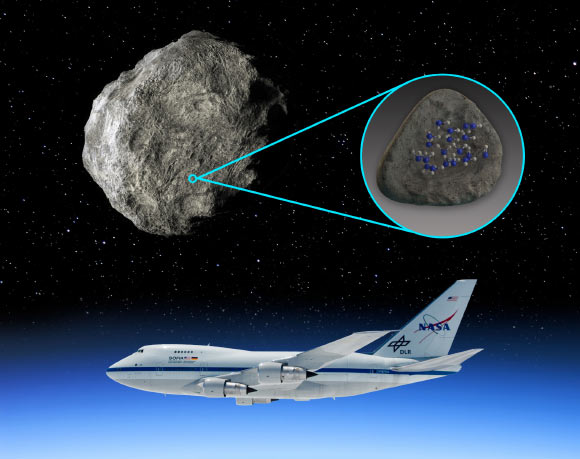
Planetary scientists using spectral data from the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope have confirmed the detection of hydroxyl molecules on the surface of the metallic asteroid Psyche. The presence of…